Standard Preparation—
Dissolve in the solvent specified in the table of
Solvents and Final Concentrations a suitable quantity of the USP Reference Standard specified in the individual monograph, previously dried under the conditions specified in the individual monograph and accurately weighed, and dilute quantitatively and stepwise with the same solvent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about that specified in the table. Pipet 2.0 mL of this solution into each of two 125-mL glass-stoppered conical flasks.
Solvents and Final Concentrations
| Antibiotic |
Solvent* |
Final
Concentration |
| Amoxicillin |
Water |
1.0 mg per mL |
| Ampicillin |
Water |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Ampicillin Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Cloxacillin Sodium |
Water |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Cyclacillin |
Water |
1.0 mg per mL |
| Dicloxacillin Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Methicillin Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Nafcillin Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
1.25 mg per mL |
| Oxacillin Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
1.25 mg per mL |
Penicillin G
 Potassium Potassium |
Buffer No. 1 |
2,000 units per mL |
| Penicillin G Sodium |
Buffer No. 1 |
2,000 units per mL |
Penicillin V
 Potassium Potassium |
Buffer No. 1 |
2,000 units per mL |
Phenethicillin
 Potassium Potassium |
Buffer No. 1 |
2,000 units per mL |
*
Unless otherwise noted, the Buffers are the potassium phosphate buffers defined in the section Media and Diluents under Antibiotics—Microbial Assays  81 81 , except that sterilization is not required before use.
|
Procedure—
Inactivation and Titration—
To 2.0 mL of the
Standard Preparation and of the
Assay Preparation, in respective flasks, add 2.0 mL of 1.0 N sodium hydroxide, mix by swirling, and allow to stand for 15 minutes. To each flask add 2.0 mL of 1.2 N hydrochloric acid, add 10.0 mL of 0.01 N iodine VS, immediately insert the stopper, and allow to stand for 15 minutes. Titrate with 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate VS. As the endpoint is approached, add 1 drop of
starch iodide paste TS, and continue the titration to the discharge of the blue color.
Blank Determination—
To a flask containing 2.0 mL of the
Standard Preparation add 10.0 mL of 0.01 N iodine VS. If the
Standard Preparation contains amoxicillin or ampicillin, immediately add 0.1 mL of 1.2 N hydrochloric acid. Immediately titrate with 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate VS. As the endpoint is approached, add 1 drop of
starch iodide paste TS, and continue the titration to the discharge of the blue color. Similarly treat a flask containing 2.0 mL of the
Assay Preparation.
Calculations—
Calculate the microgram (or unit) equivalent (
F) of each mL of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed by the
Standard Preparation by the formula:
(2
CP) / (
B 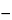 I
I),
in which
C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Reference Standard in the
Standard Preparation, P is the potency, in µg (or units) per mg, of the Reference Standard,
B is the volume, in mL, of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the
Blank determination, and
I is the volume, in mL, of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the
Inactivation and titration. Calculate the potency of the specimen under test by the formula given in the individual monograph.